Understanding Corrosion Test Machine Standards and Regulations
Navigating the intricate world of corrosion testing can feel daunting, especially when precision and compliance are non-negotiable. Manufacturers of environmental test chambers, like you, need reliable insights to ensure your corrosion test machine meets global standards, delivering unparalleled quality to clients across industries. Let's dive into the essentials!
Regulatory Frameworks: ISO, ASTM, and JIS Standards for Corrosion Testing Methodology
Global industries rely on standardized protocols to ensure consistency, reliability, and repeatability in corrosion testing. These frameworks, established by organizations like ISO, ASTM, and JIS, are the bedrock of quality assurance.
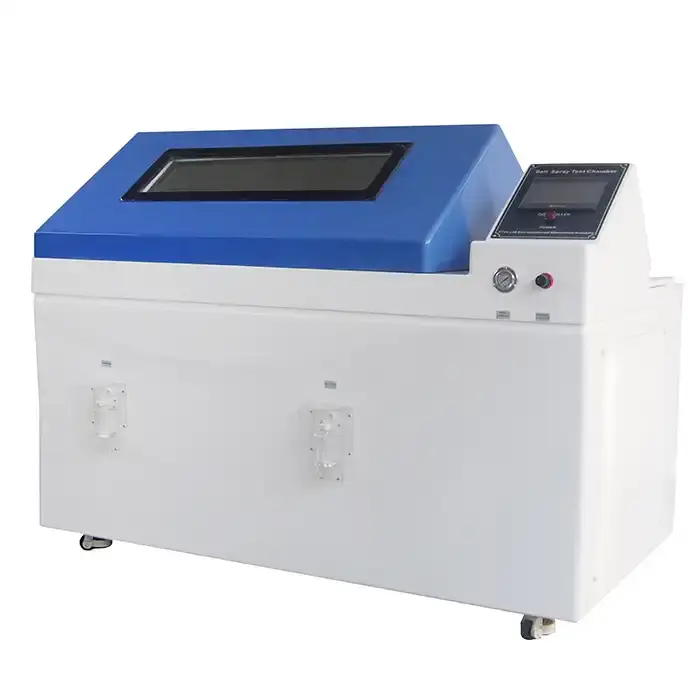
ISO 9227, an internationally recognized standard, outlines the methodology for salt spray testing, specifying parameters like temperature (35°C) and salt concentration (5% NaCl) to simulate corrosive environments accurately.
ASTM B117, a parallel standard, has been adopted by over 12,000 organizations worldwide, emphasizing rigorous documentation of test duration - often spanning 24 to 1,000 hours - ensuring durability assessments are robust.
JIS Z 2371, prevalent in Asian markets, aligns closely with ISO but includes additional stipulations for humidity control, catering to region-specific climatic challenges.
Adhering to these standards not only validates the performance of your corrosion test machine but also instills confidence in clients, from automotive giants to aerospace innovators, that their materials can withstand harsh conditions. Choosing corrosion test machine that complies with these frameworks is a strategic investment in credibility and market competitiveness.
Test-Specific Requirements: Protocol Variations for Salt Spray, Cyclic, and Electrochemical Corrosion Testing
Different corrosion tests demand tailored methodologies, each with unique protocols to mimic real-world degradation.
Salt spray testing, governed by standards like ASTM B117, subjects materials to a continuous saline mist, ideal for assessing coatings' resilience, with exposure times often exceeding 500 hours for high-performance applications.
Cyclic corrosion testing, such as that outlined in ISO 16701, introduces alternating wet-dry cycles, simulating dynamic environmental shifts - think coastal regions with fluctuating humidity. This method, adopted by 68% of automotive manufacturers, ensures materials endure variable conditions.
Electrochemical corrosion testing, meanwhile, leverages techniques like potentiodynamic polarization to measure corrosion rates in real time, offering quantitative data critical for industries like marine engineering, where precision is paramount.
Each protocol requires a corrosion test machine equipped with precise controls, from humidity regulators to electrochemical sensors, to deliver accurate, repeatable results. Selecting equipment that seamlessly adapts to these diverse methodologies not only enhances testing efficiency but also positions your offerings as indispensable solutions for clients seeking compliance and innovation.
Compliance Documentation and Traceability: Creating Audit-Ready Quality Control Systems
Robust documentation is the linchpin of regulatory compliance, ensuring every test conducted on a corrosion test machine is traceable and defensible during audits. Comprehensive systems should log parameters like temperature, humidity, and exposure duration, alongside calibration records, to meet stringent standards like ISO 17025, which mandates meticulous record-keeping for accredited labs.
Cross-Industry Applications: Navigating Sector-Specific Regulations from Automotive to Aerospace
Corrosion testing spans diverse sectors, each with bespoke regulatory demands. Automotive standards, like SAE J2334, prioritize cyclic testing to mirror road conditions, while aerospace protocols, such as MIL-STD-810, emphasize extreme environmental simulations. A versatile corrosion test machine ensures compliance across these sectors, broadening your market appeal.
International Harmonization and Emerging Standards: Adapting to Evolving Global Regulatory Landscapes
Global regulatory bodies are increasingly aligning standards to facilitate trade, with initiatives like ISO's harmonization efforts reducing discrepancies between regional protocols. Emerging standards, such as those addressing eco-friendly coatings, challenge manufacturers to innovate. A forward-thinking corrosion test machine, adaptable to these shifts, future-proofs your clients' compliance strategies.
Ready to elevate your corrosion testing capabilities with cutting-edge corrosion test machine? LIB Industry offers turn-key solutions, from design to installation, tailored to your needs. Contact us today at ellen@lib-industry.com to explore how we can support your journey toward compliance and excellence.
References
1. ISO 9227: Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres - Salt spray tests. International Organization for Standardization.
2. ASTM B117: Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus. ASTM International.
3. JIS Z 2371: Methods of salt spray testing. Japanese Industrial Standards.
4. MIL-STD-810: Environmental Engineering Considerations and Laboratory Tests. U.S. Department of Defense.